-40%
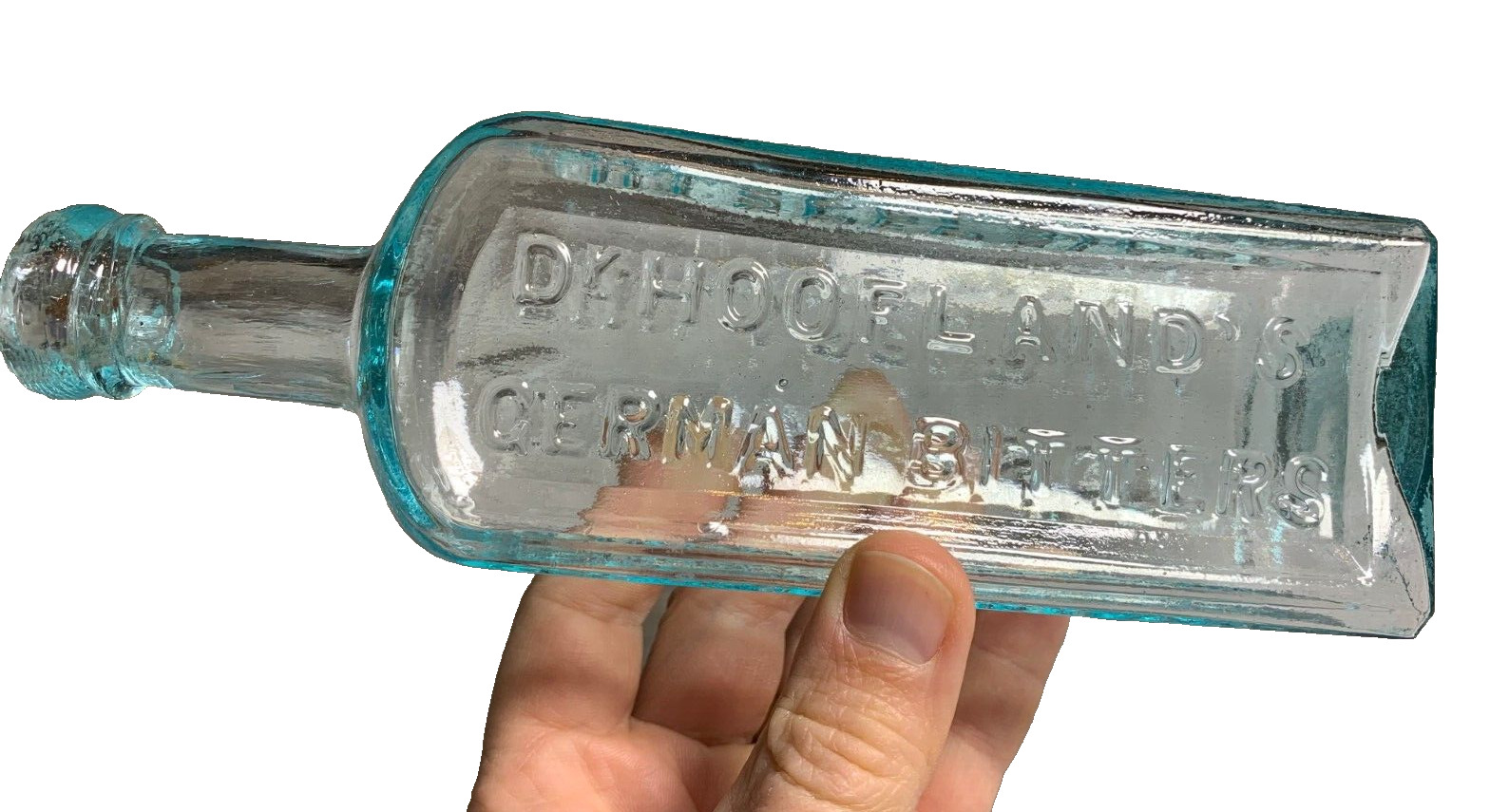
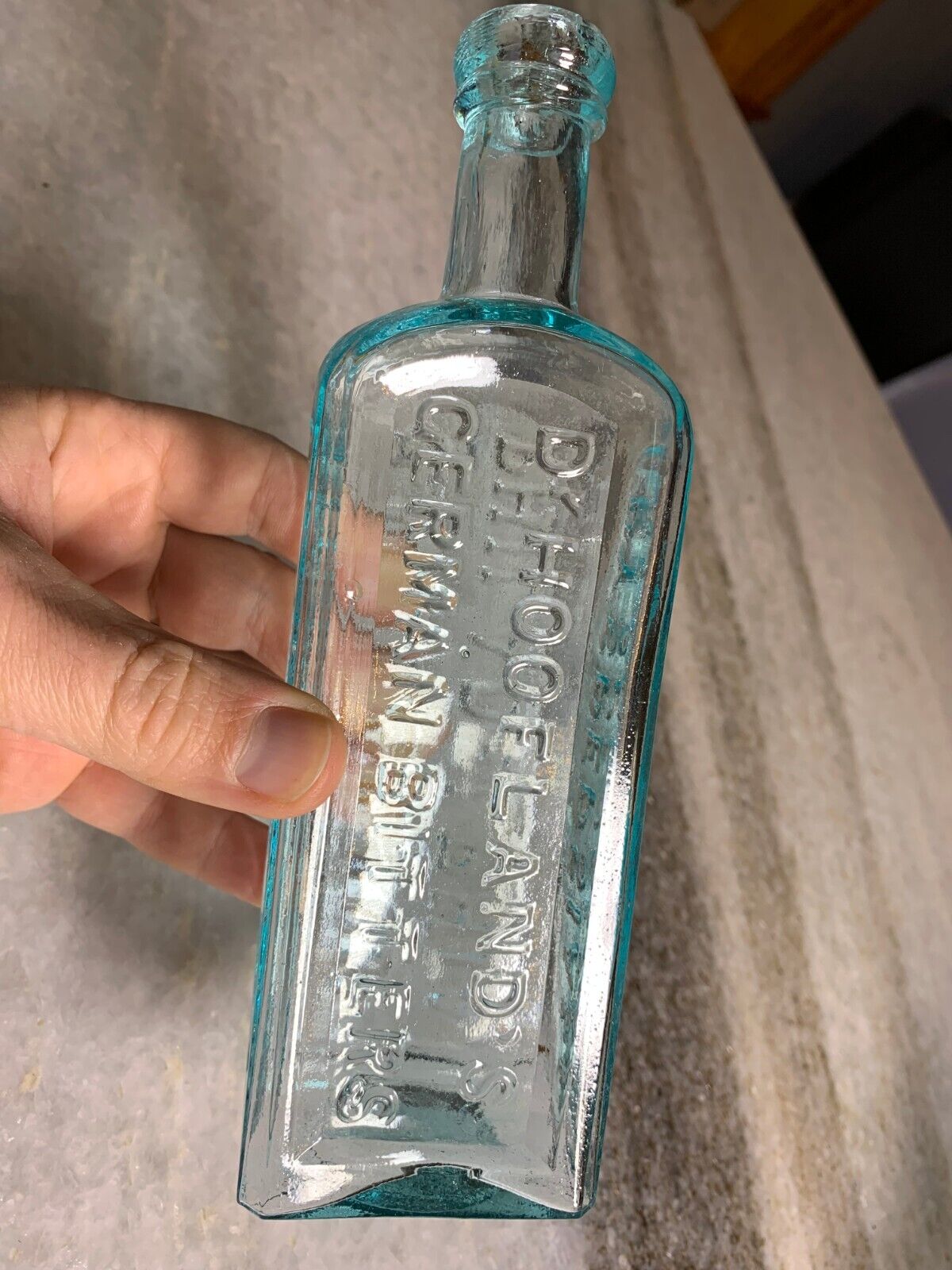
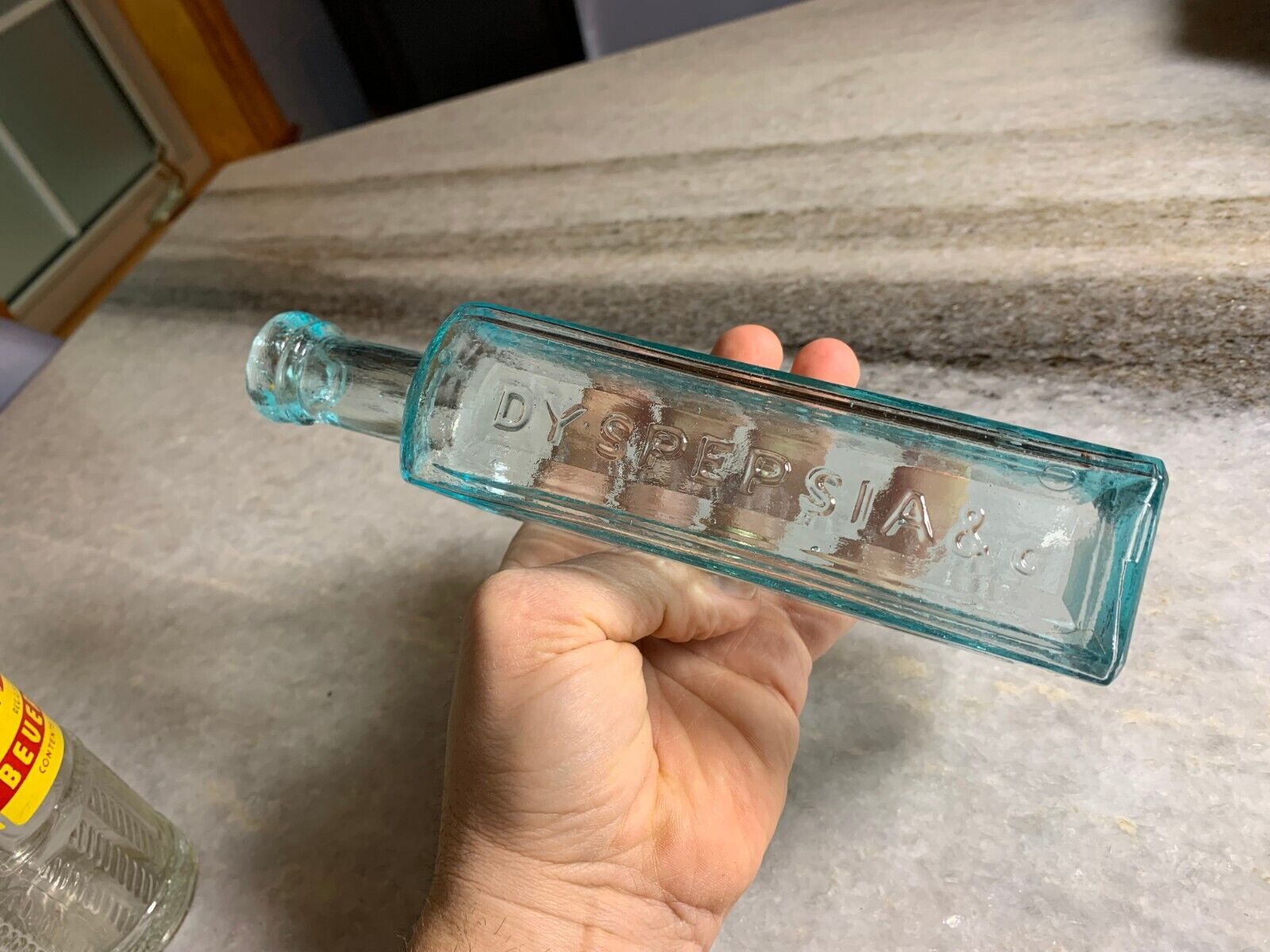
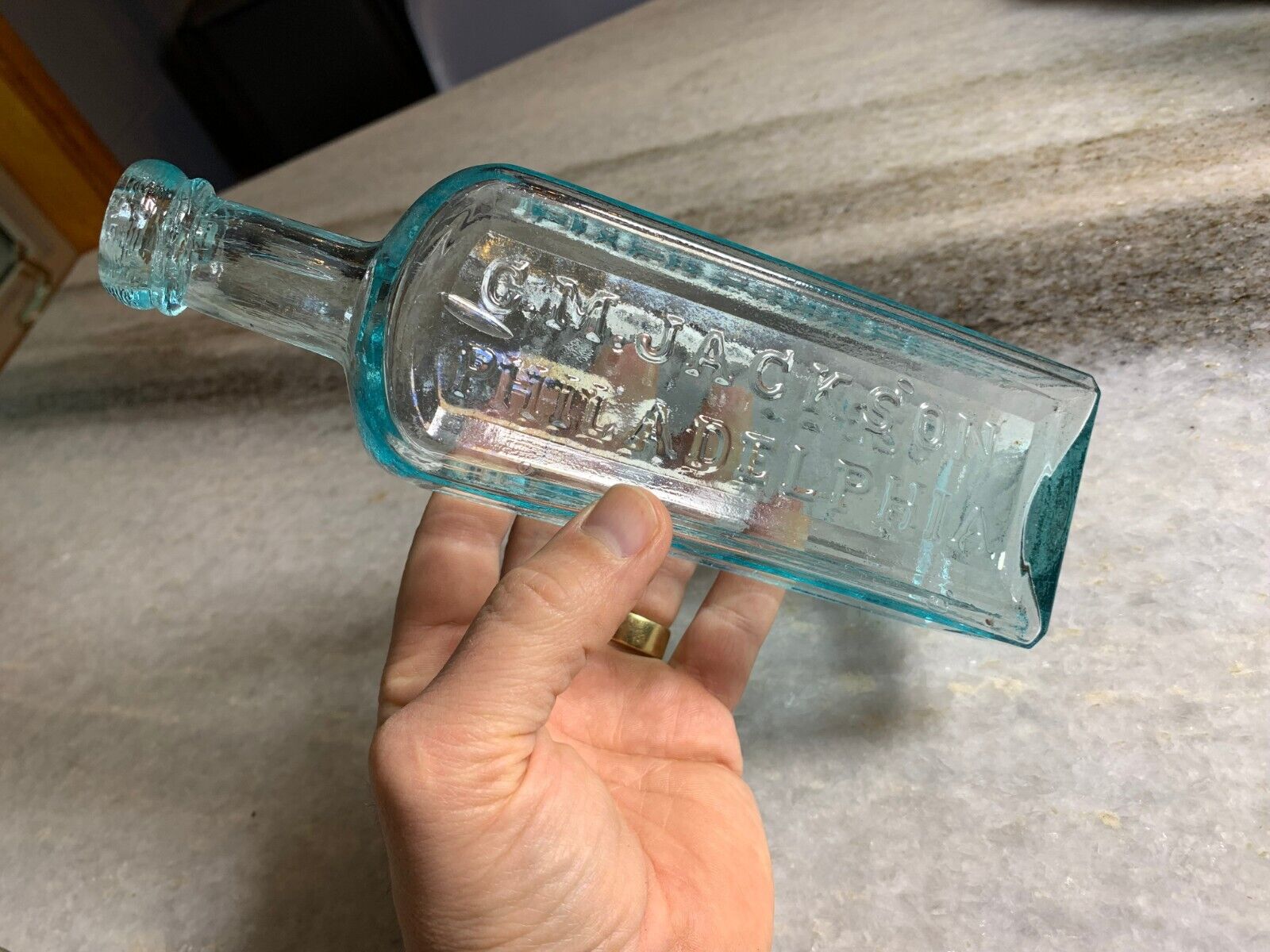
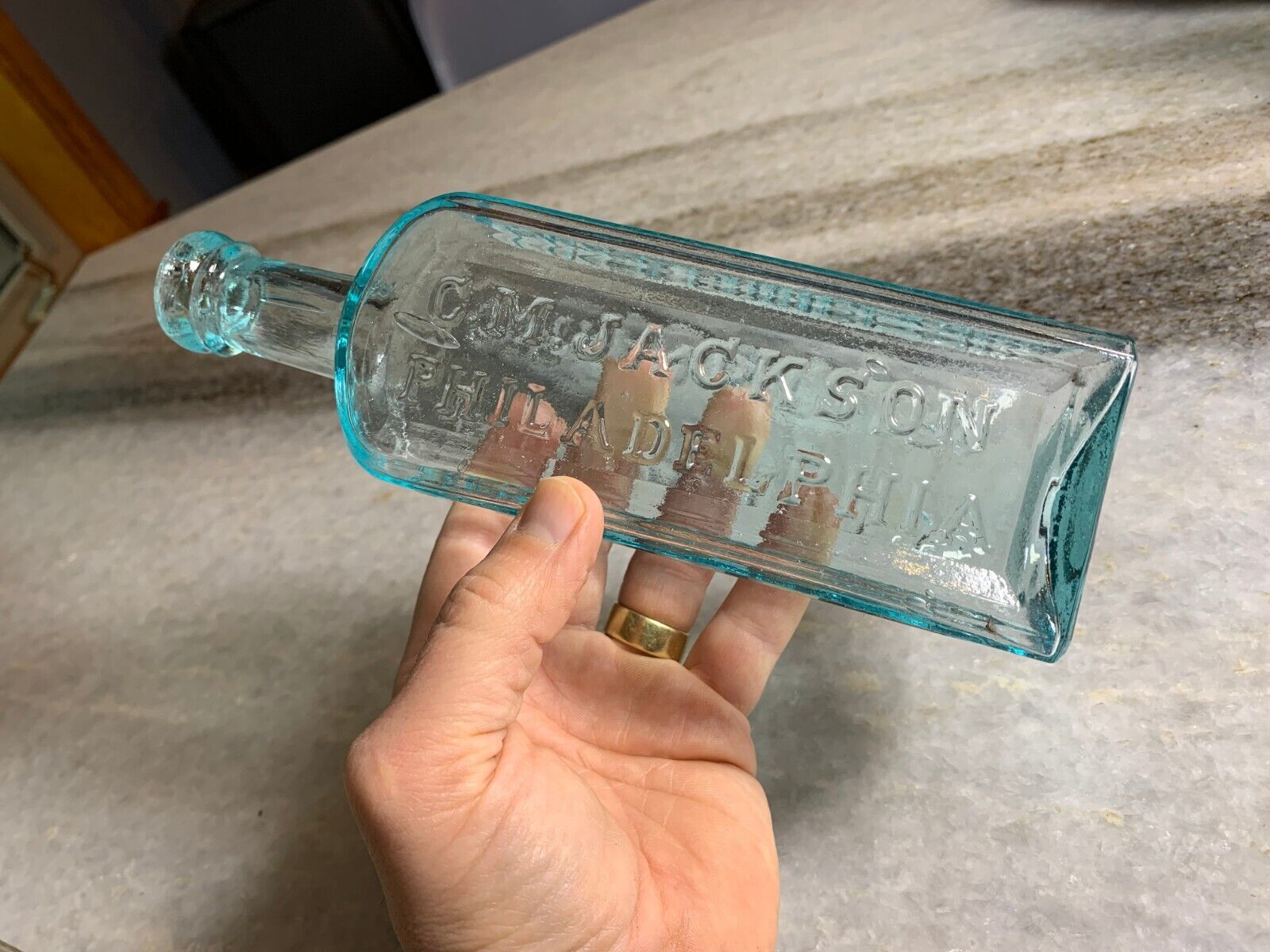
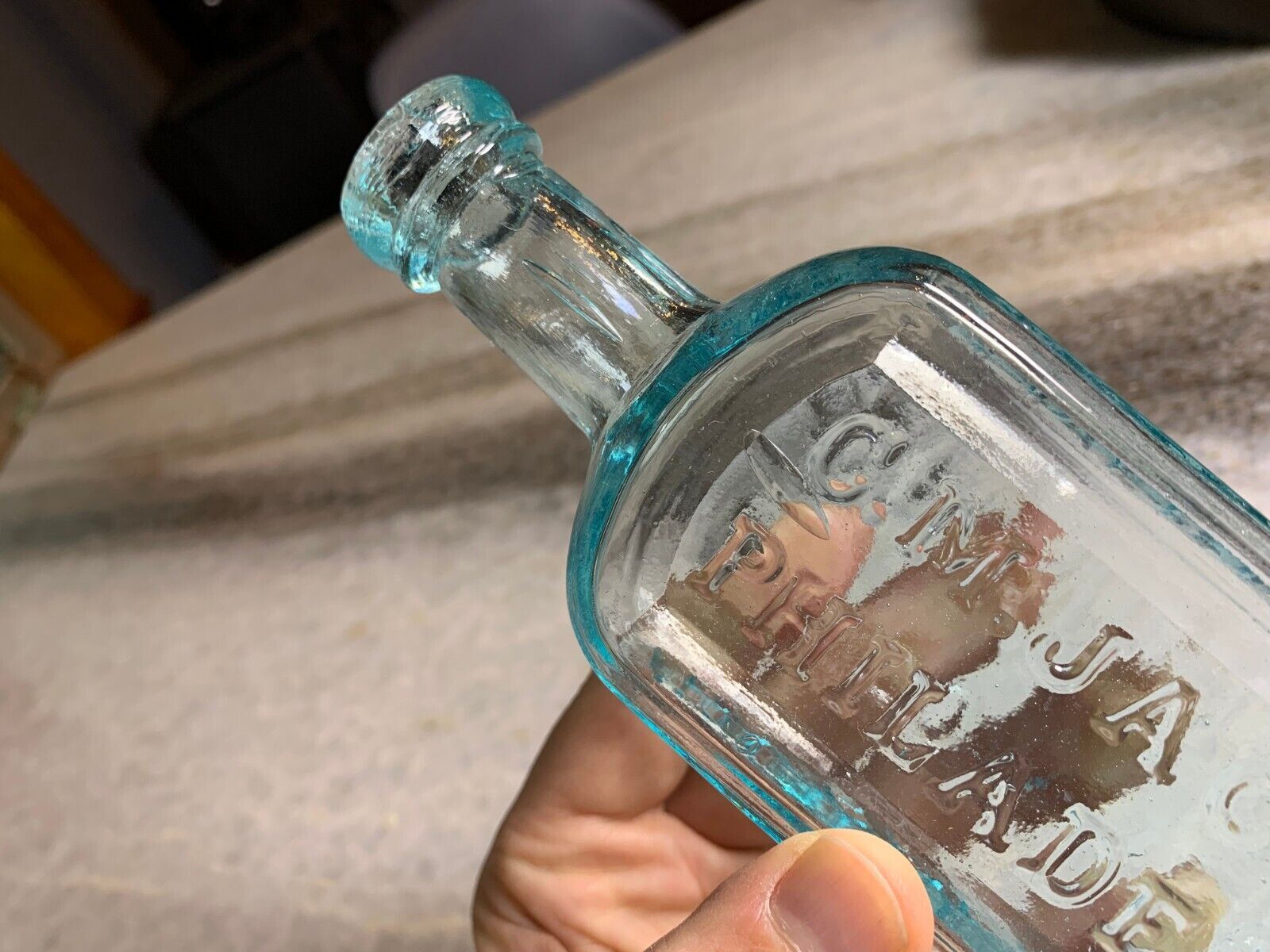
Antique Medicine Bottle Hoofland's German Bitters Liver Complaint Philadelphia!
$ 75.75
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
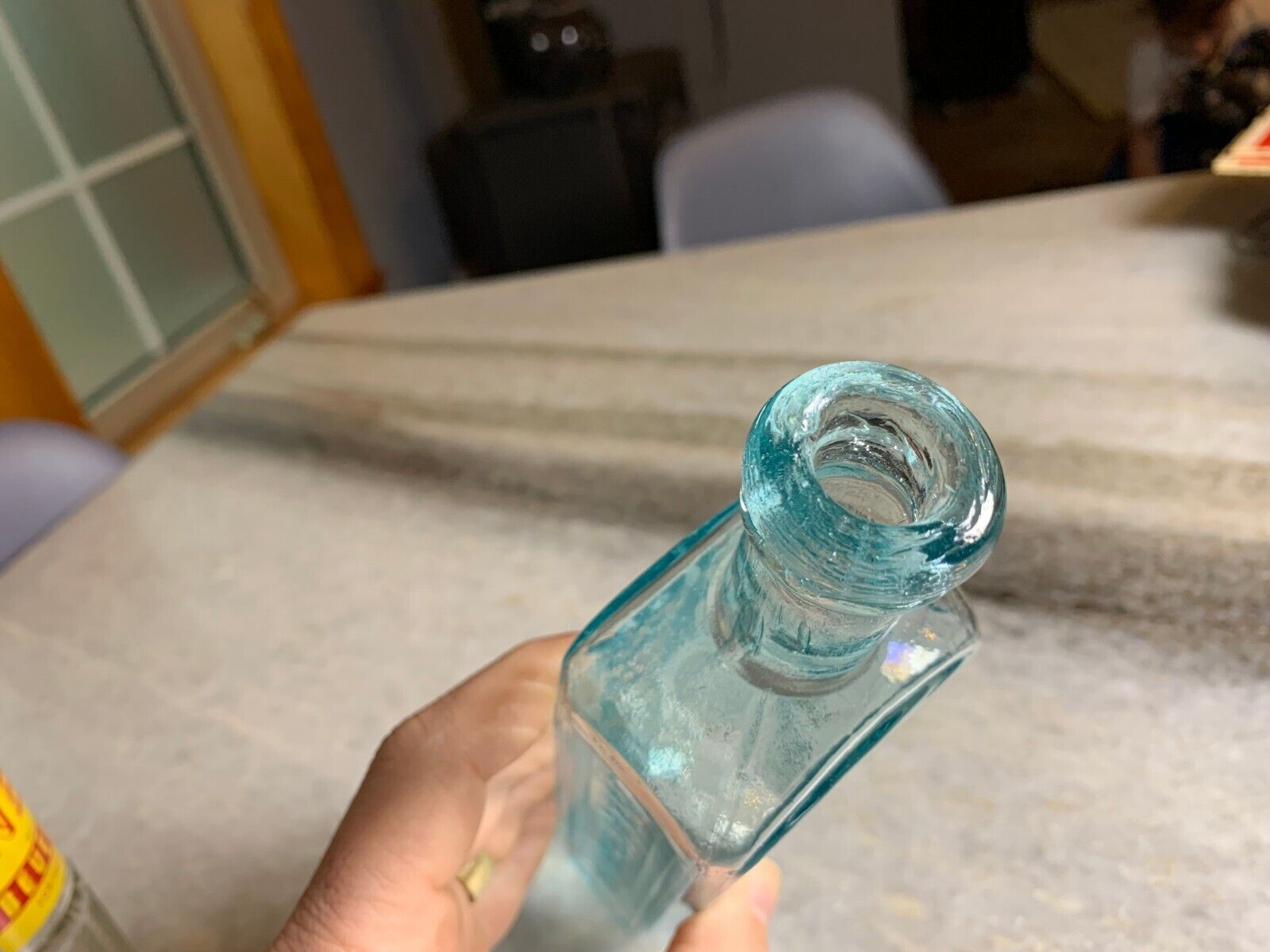
Antique , 1850sVery clean! Bright, Shiny! No ghosting. No cracks, no scratches.
Iron Pontil Mark
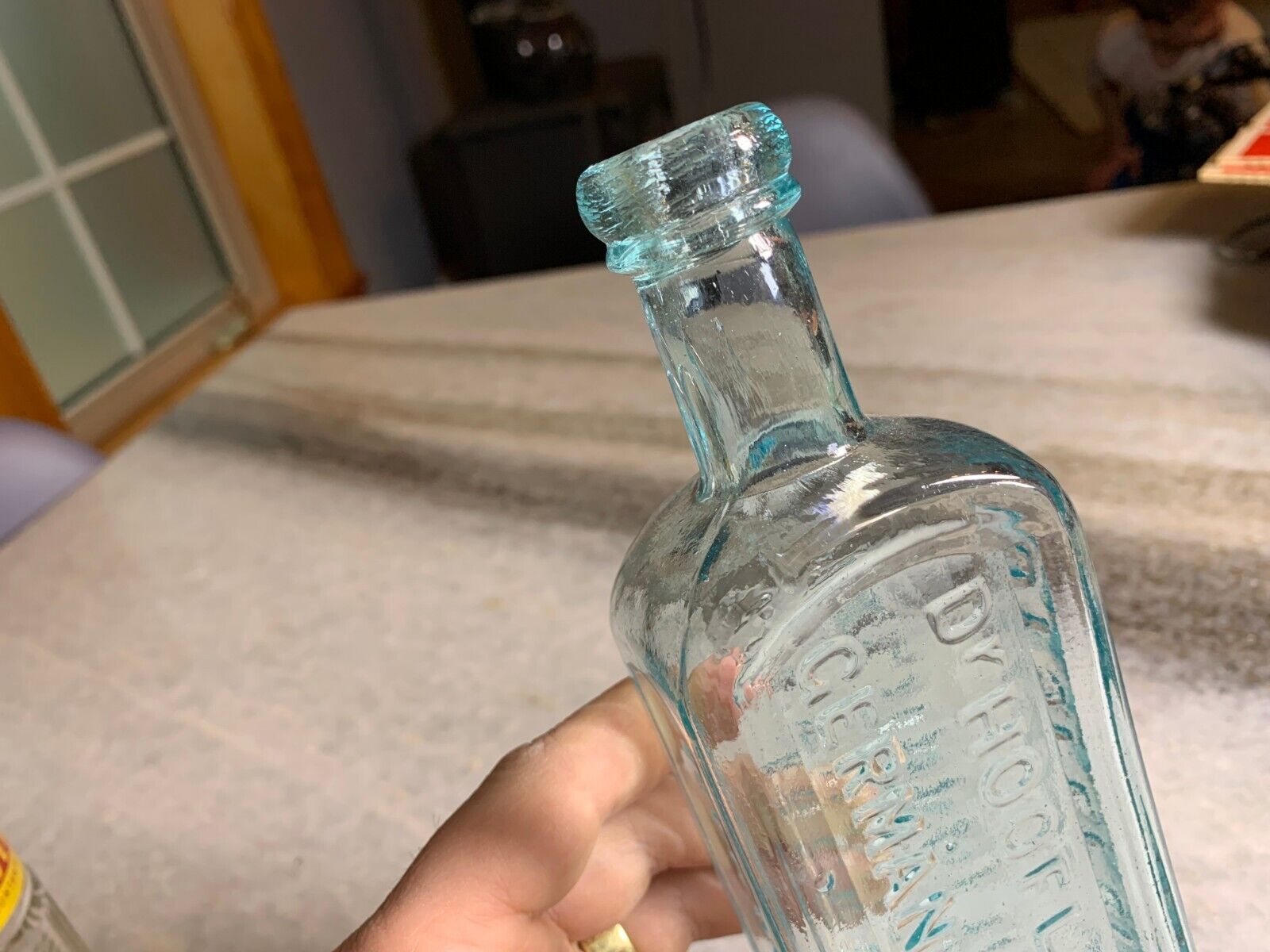
Double Ring Applied collar / Top.. I love the little bit of "oozing" that makes the glass look like its still about to drip.
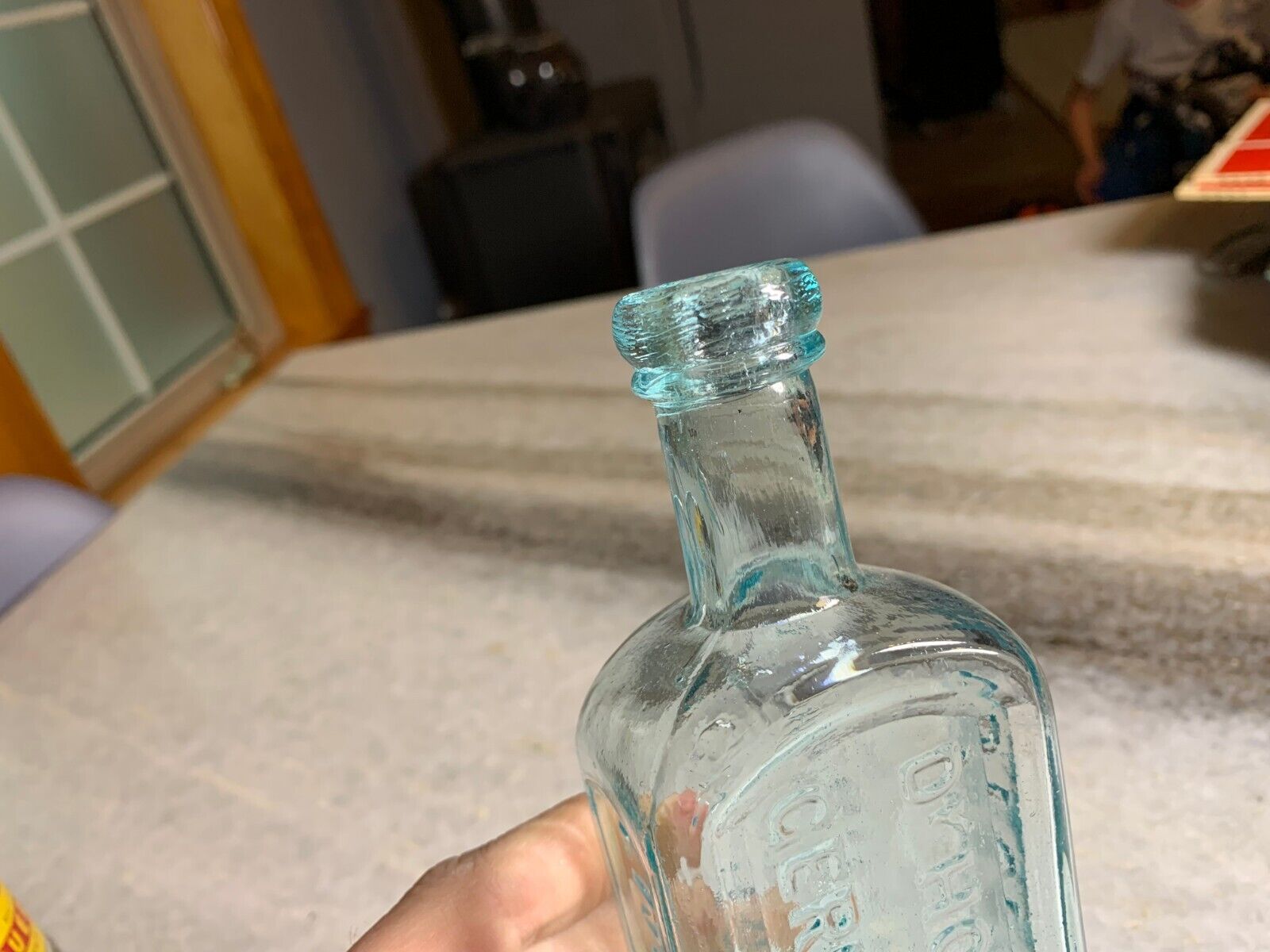
Dr. Hoofland’s
German Bitters
Liver Complaint
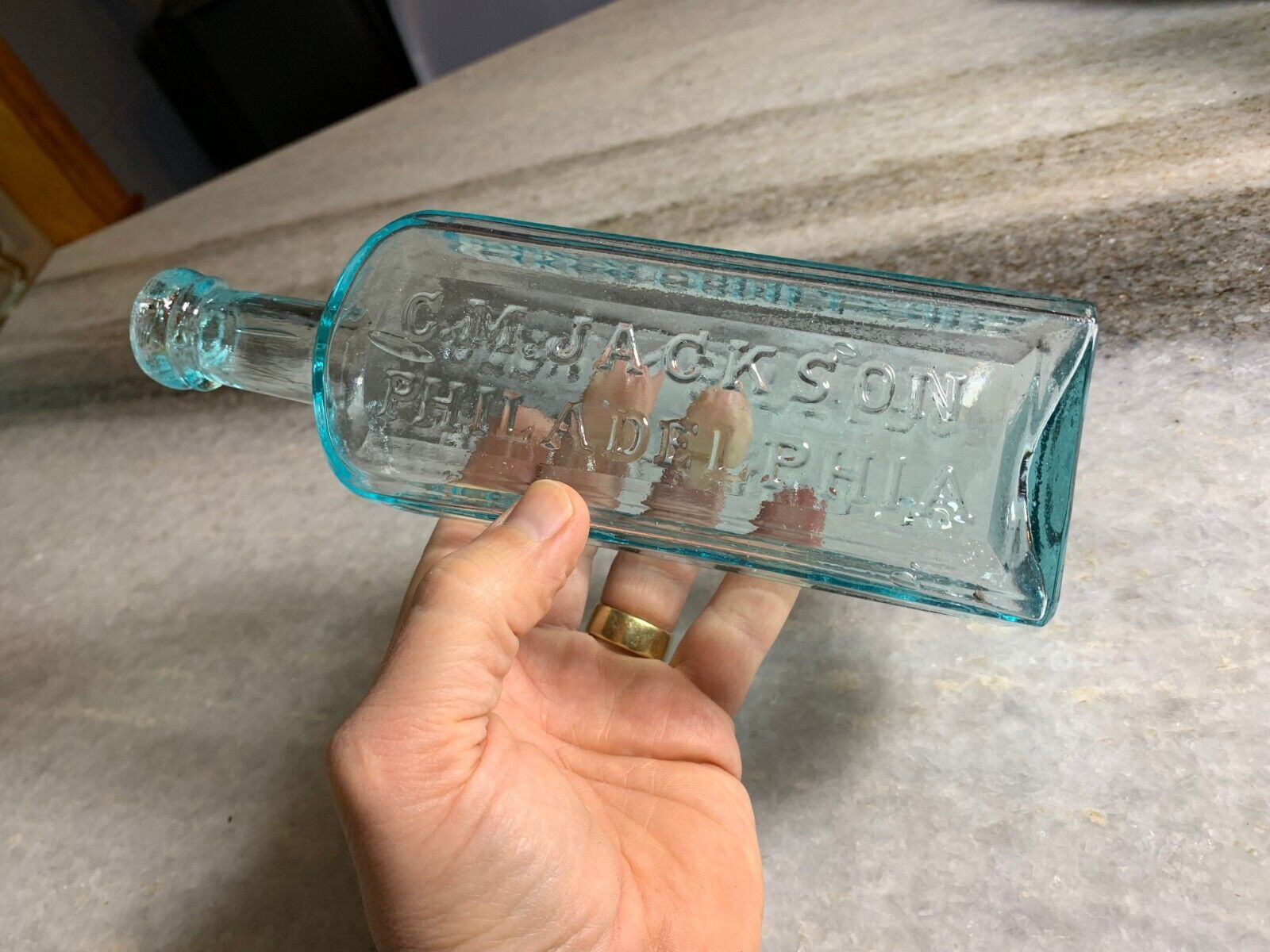
C.M. Jackson
Philadelphia
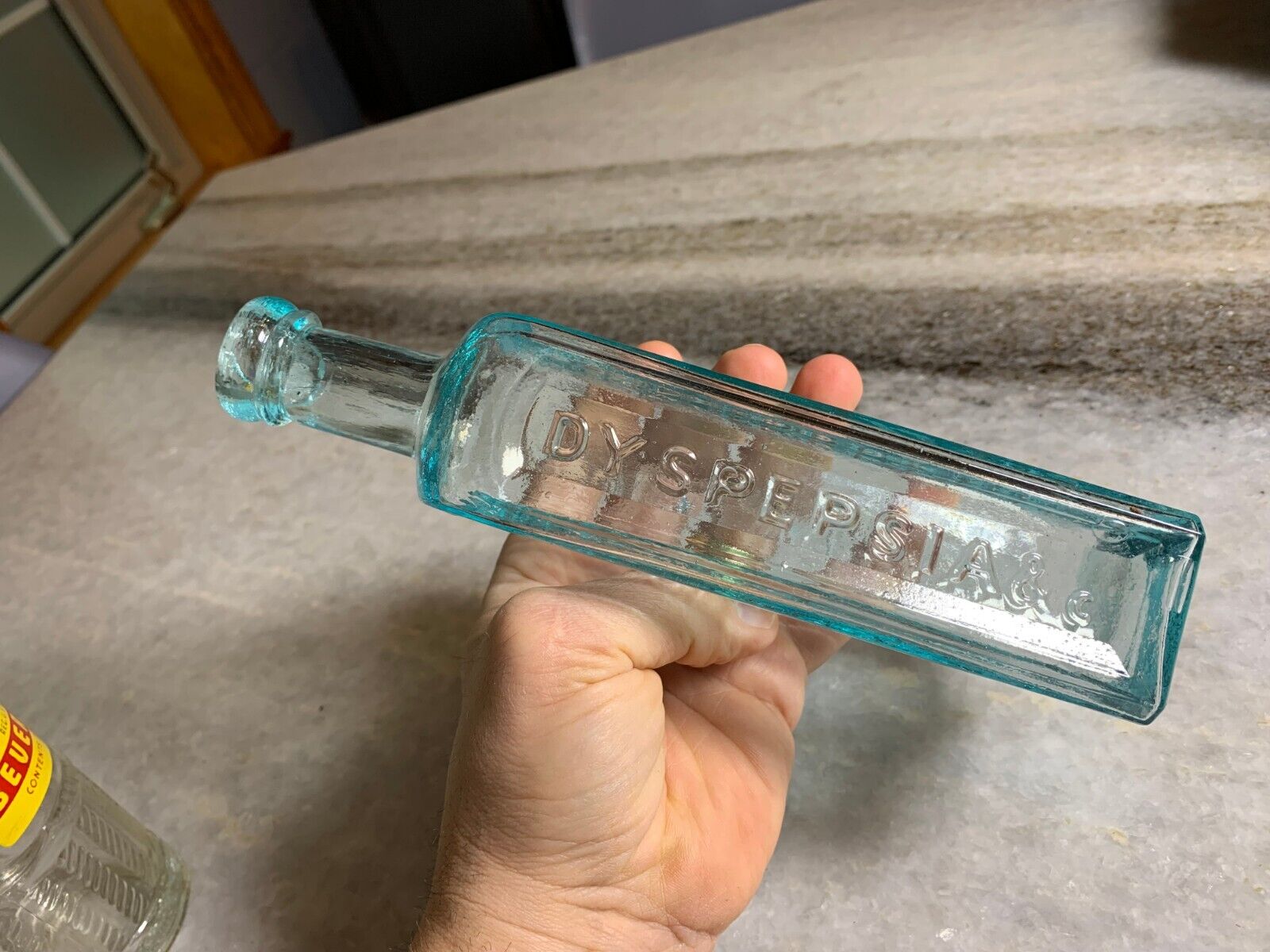
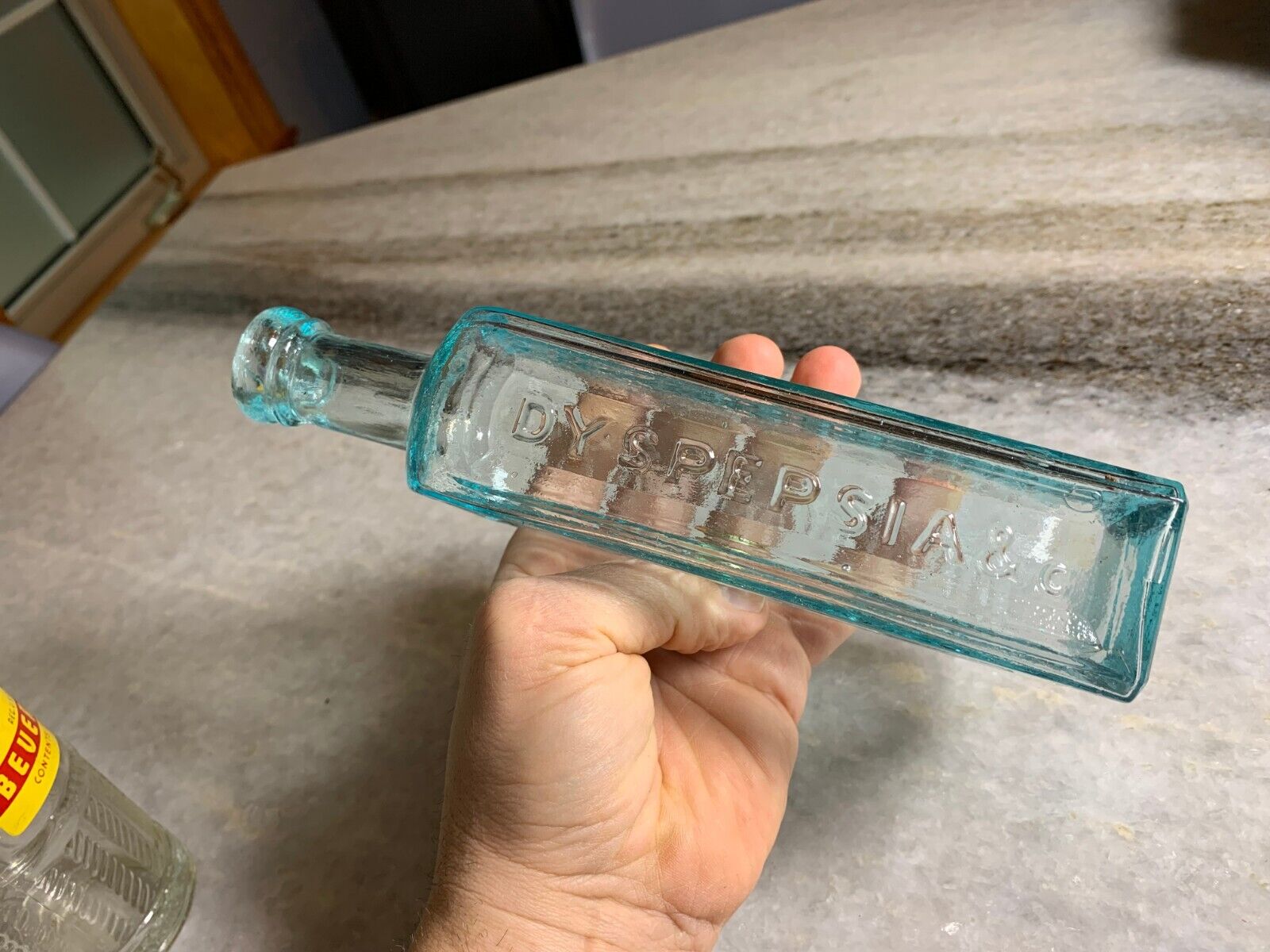
For the treament of "Dyspepsia" aka upset stomach... which was common during this time period.. if you've ever watched the "The Food that Built America" you'll note that many of the modern day house hold names like Krafts, Hersey's, Heinz, etc. came from a time period were you couldnt trust what was in your food. e.g. Whiskey was being cut with formaldehyde. It was very common like 30-40% of folks to get stomach cancer.
8.25" T
Indigestion
44 languages
Article
Talk
Read
Edit
View history
Tools
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
"Dyspepsia" redirects here. For the Negativland album, see
Dispepsi
.
Indigestion
Other names
Dyspepsia
Specialty
Gastroenterology
Symptoms
Upper abdominal pain
[1]
Frequency
Common
[1]
Indigestion
, also known as
dyspepsia
or
upset stomach
, is a condition of impaired
digestion
.
[2]
Symptoms may include upper
abdominal fullness
,
heartburn
,
nausea
,
belching
, or upper
abdominal pain
.
[3]
People may also experience
feeling full
earlier than expected when eating.
[4]
Indigestion is relatively common, affecting 20% of people at some point during their life, and is frequently caused by
gastroesophageal reflux disease
(GERD) or
gastritis
.
[1]
[5]
Indigestion is subcategorized as "organic" or "functional", but making the diagnosis can prove challenging for physicians.
[6]
Organic indigestion is the result of an underlying disease, such as
gastritis
,
peptic ulcer disease
(an ulcer of the stomach or
duodenum
), or
cancer
.
[6]
Functional indigestion (previously called non-ulcer dyspepsia)
[7]
is indigestion without evidence of underlying disease.
[8]
Functional indigestion is estimated to affect about 15% of the general population in western countries and accounts for a majority of dyspepsia cases.
[7]
[9]
In patients who are 60 or older, or who have worrisome symptoms such as trouble swallowing, weight loss, or blood loss, an
endoscopy
(a procedure whereby a camera attached to a flexible tube is inserted down the throat and into the stomach) is recommended to further assess and find a potential cause.
[1]
In patients younger than 60 years of age, testing for the bacteria
H. pylori
and if positive, treatment of the infection is recommended.
[1]
More details about how indigestion is diagnosed and treated can be found below.
Signs and symptoms
[
edit
]
Symptoms
[
edit
]
Patients experiencing indigestion likely report one, a combination of, or all of the following symptoms:
[6]
[10]
upper abdominal pain or discomfort
bloating
early
satiety
postprandial
fullness
nausea with or without vomiting
anorexia
regurgitation
belching
Signs
[
edit
]
There may be abdominal tenderness, but this finding is nonspecific and is not required to make a diagnosis.
[10]
However, there are physical exam signs that may point to a different diagnosis and underlying cause for a patient's reported discomfort. A positive Carnett sign (focal tenderness that increases with abdominal wall contraction and palpation) suggests an
etiology
involving the abdominal wall musculature.
Cutaneous
dermatomal distribution of pain may suggest a
thoracic
polyradiculopathy
. Tenderness to palpation over the right upper quadrant, or Murphy's sign, may suggest
cholecystitis
or gallbladder inflammation.
[11]
Alarm symptoms
[
edit
]
Also known as
Alarm features
,
alert features
,
red flags
, or
warning signs
in gastrointestinal (GI) literature.
Alarm features are thought to be associated with serious gastroenterologic disease and include:
[12]
chronic gastrointestinal bleeding
progressive unintentional weight loss
progressive difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
persistent vomiting
Iron deficiency anemia
Vitamin B
12
deficiency
(
Pernicious anemia
)
epigastric
mass
Cause
[
edit
]
Indigestion is a diagnosis related to a combination of symptoms that can be attributed to "organic" or "functional" causes.
[13]
Organic dyspepsia should have pathological findings upon endoscopy, like an ulcer in the stomach lining in
peptic ulcer disease
.
[13]
Functional dyspepsia is unlikely to be detected on endoscopy but can be broken down into two subtypes, epigastric pain syndrome (EPS) and post-prandial distress syndrome (PDS).
[14]
In addition, indigestion could be caused by medications, food, or other disease processes.
Psychosomatic and cognitive factors are important in the evaluation of people with chronic dyspepsia. Studies have shown a high occurrence of mental disorders, notably anxiety and depression, amongst patients with dyspepsia; however, there is little evidence to prove causation.
[15]
Organic dyspepsia
[
edit
]
Esophagitis
[
edit
]
Esophagitis
is an inflammation of the esophagus, most commonly caused by gastroesophageal reflux disease (
GERD
).
[6]
It is defined by the sensation of "
heartburn
" or a burning sensation in the chest as a result of inappropriate relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter at the site where the esophagus connects to the stomach. It is often treated with proton pump inhibitors. If left untreated, the chronic damage to the esophageal tissues poses a risk of developing cancer.
[6]
A meta-analysis showed risk factors for developing GERD included age equal to or greater than 50, smoking, the use of non-steroid anti-inflammatory medications, and obesity.
[16]
Gastritis
[
edit
]
Common causes of
gastritis
include peptic ulcer disease, infection, or medications.
Peptic ulcer disease
[
edit
]
Gastric and duodenal ulcers are the defining feature of
peptic ulcer disease
(PUD). PUD is most commonly caused by an infection with
H. pylori
or
NSAID
use.
[17]
Helicobacter pylori
(
H. pylori
) infection
[
edit
]
The role of
H. pylori
in functional dyspepsia is controversial, and treatment for
H. pylori
may not lead to complete improvement of a patient's dyspepsia.
[6]
However, a recent systemic review and meta-analysis of 29 studies published in 2022 suggests that successful treatment of
H. pylori
modestly improves indigestion symptoms.
[18]
Pancreatobiliary disease
[
edit
]
These include
cholelithiasis
,
chronic pancreatitis
, and
pancreatic cancer
.
Duodenal micro-inflammation
[
edit
]
Duodenal
micro-inflammation caused by an altered duodenal
gut microbiota
, reactions to foods (mainly
gluten
proteins) or infections may induce dyspepsia symptoms in a subset of people.
[19]
Functional dyspepsia
[
edit
]
Functional dyspepsia is a common cause of
chronic
heartburn. More than 70% of people have no obvious organic cause for their symptoms after evaluation.
[13]
Symptoms may arise from a complex interaction of increased visceral afferent sensitivity, gastric delayed emptying (
gastroparesis
) or impaired accommodation to food. Diagnostic criteria for functional dyspepsia categorize it into two subtypes by symptom: epigastric pain syndrome and post-prandial distress syndrome.
[14]
Anxiety
is also associated with functional dyspepsia. In some people, it appears before the onset of gut symptoms; in other cases, anxiety develops after onset of the disorder, which suggests that a
gut-driven brain
disorder may be a possible cause.
[14]
Although benign, these symptoms may be chronic and difficult to treat.
[20]
Epigastric pain syndrome (EPS)
[
edit
]
Defined by stomach pain and/or burning that interferes with daily life, without any evidence of organic disease.
[21]
Post-prandial distress syndrome (PDS)
[
edit
]
Defined by post-prandial fullness or early satiation that interferes with daily life, without any evidence of organic disease.
[21]
Food, herb, or drug intolerance
[
edit
]
Acute, self-limited dyspepsia may be caused by
overeating
, eating too quickly, eating high-fat foods, eating during stressful situations, or drinking too much alcohol or coffee. Many medications cause dyspepsia, including
aspirin
,
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
(NSAIDs),
antibiotics
(
metronidazole
,
macrolides
), bronchodilators (theophylline), diabetes drugs (
acarbose
,
metformin
,
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitor
,
amylin analogs
,
GLP-1
receptor antagonists), antihypertensive medications (angiotensin converting enzyme [ACE] inhibitors,
Angiotensin II receptor antagonist
), cholesterol-lowering agents (
niacin
,
fibrates
), neuropsychiatric medications (cholinesterase inhibitors [donepezil, rivastigmine]),
SSRIs
(
fluoxetine
,
sertraline
),
serotonin
-norepinephrine-reuptake inhibitors (
venlafaxine
,
duloxetine
), Parkinson drugs (
Dopamine agonist
,
monoamine oxidase
[MAO]-B inhibitors), weight-loss medications (orlistat),
corticosteroids
,
estrogens
,
digoxin
,
iron
, and
opioids
.
[22]
[23]
Common herbs have also been shown to cause indigestion, like white willow berry,
garlic
,
ginkgo
, chaste tree berry,
saw palmetto
, and
feverfew
.
[22]
Studies have shown that wheat and dietary fats can contribute to indigestion and suggest foods high in short-chain carbohydrates (
FODMAP
) may be associated with dyspepsia.
[24]
This suggests reducing or consuming a
gluten-free
, low-fat, and/or
FODMAP diet
may improve symptoms.
[24]
[25]
Additionally, some people may experience dyspepsia when eating certain spices or spicy food as well as foods like peppers, chocolate, citrus, and fish.
[6]
Systemic diseases
[
edit
]
There are a number of
systemic diseases
that may involve dyspepsia, including
coronary disease
,
congestive heart failure
,
diabetes mellitus
,
hyperparathyroidism
,
thyroid disease
, and
chronic kidney disease
.
Post-infectious causes of dyspepsia
[
edit
]
Gastroenteritis
increases the risk of developing chronic dyspepsia. Post-infectious dyspepsia is the term given when dyspepsia occurs after an acute gastroenteritis infection. It is believed that the underlying causes of post-infectious
IBS
and post-infectious dyspepsia may be similar and represent different aspects of the same pathophysiology.
[26]
Pathophysiology
[
edit
]
The pathophysiology for indigestion is not well understood; however, there are many theories. For example, there are studies that suggest a gut-brain interaction, as patients who received an antibiotic saw a reduction in their indigestion symptoms.
[27]
Other theories propose issues with gut motility, a hypersensitivity of gut viscera, and imbalance of the microbiome.
[9]
A genetic predisposition is plausible, but there is limited evidence to support this theory.
[28]
Diagnosis
[
edit
]
Simplified diagram of how indigestion is diagnosed and treatment(s) determined
A diagnosis for indigestion is based on symptoms, with a possible need for more diagnostic tests. In younger patients (less than 60 years of age) without red flags (e.g., weight loss), it is recommended to test for H. pylori noninvasively, followed by treatment with antibiotics in those who test positively. A negative test warrants discussing additional treatments, like proton pump inhibitors, with your doctor.
[1]
An upper GI endoscopy may also be recommended.
[29]
In older patients (60 or older), an endoscopy is often the next step in finding out the cause of newly onset indigestion regardless of the presence of alarm symptoms.
[1]
However, for all patients regardless of age, an official diagnosis requires symptoms to have started at least 6 months ago with a frequency of at least once a week over the last 3 months.
[10]
Treatment
[
edit
]
Functional and organic dyspepsia have similar treatments. Traditional therapies used for this diagnosis include lifestyle modification (e.g., diet),
antacids
,
proton-pump inhibitors
(PPIs),
H
2
-receptor antagonists (H2-RAs)
,
prokinetic
agents, and
antiflatulents
. PPIs and H2-RAs are often first-line therapies for treating dyspepsia, having shown to be better than placebo medications.
[30]
Anti-depressants, notably tricyclic antidepressants, have been tested on patients who do not respond to traditional therapies with some benefits, though the research is of poor quality and adverse affects are noted.
[30]
Diet
[
edit
]
A lifestyle change that may help with indigestion is a change in diet, such as a stable and consistent eating schedule and slowing the pace of eating.
[31]
Additionally, there are studies that support a reduction in the consumption of fats may also alleviate dyspepsia.
[31]
While some studies suggest a correlation between dyspepsia and celiac disease, not everyone with indigestion needs to refrain from gluten in their diet. However, a
gluten-free diet
can relieve the symptoms in some patients without celiac disease.
[19]
[31]
Lastly, a
FODMAPs
diet or diet low/free from certain complex sugars and sugar alcohols has also been shown to be potentially beneficial in patients with indigestion.
[31]
Acid suppression
[
edit
]
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) were found to be better than placebo in a literature review, especially when looking at long-term symptom reduction.
[32]
[33]
H2 receptor antagonists (H2-RAs) have similar effect on symptoms reduction when compared to PPIs.
[32]
However, there is little evidence to support prokinetic agents are an appropriate treatment for dyspepsia.
[34]
Currently, PPIs are FDA indicated for erosive
esophagitis
, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD),
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
, eradication of H. pylori, duodenal and gastric ulcers, and NSAID-induced ulcer healing and prevention, but not functional dyspepsia.
[35]
Prokinetics
[
edit
]
Prokinetics
(medications focused on increasing gut motility), such as
metoclopramide
or
erythromycin
, has a history of use as a secondary treatment for dyspepsia.
[6]
While multiple studies show that it is more effective than placebo, there are multiple concerns about the side effects surrounding the long-term use of these medications.
[6]
Alternative medicine
[
edit
]
A 2021
meta-analysis
concluded that herbal remedies, like menthacarin (a combination of
peppermint
and
caraway
oils),
ginger
, artichoke,
licorice
, and jollab (a combination of
rose water
,
saffron
, and candy sugar), may be as beneficial as conventional therapies when treating dyspepsia symptoms.
[36]
However, it is important to note that herbal products are not regulated by the FDA and therefore it is difficult to assess the quality and safety of the ingredients found in alternative medications.
[37]
Epidemiology
[
edit
]
Indigestion is a common problem and frequent reason for primary care physicians to refer patients to GI specialists.
[38]
Worldwide, dyspepsia affects about a third of the population.
[39]
It can affect a person's quality of life even if the symptoms within themselves are usually not life-threatening. Additionally, the financial burden on the patient and healthcare system is costly - patients with dyspepsia were more likely to have lower work productivity and higher healthcare costs compared to those without indigestion.
[40]
Risk factors include NSAID-use, H. pylori infection, and smoking.
[41]